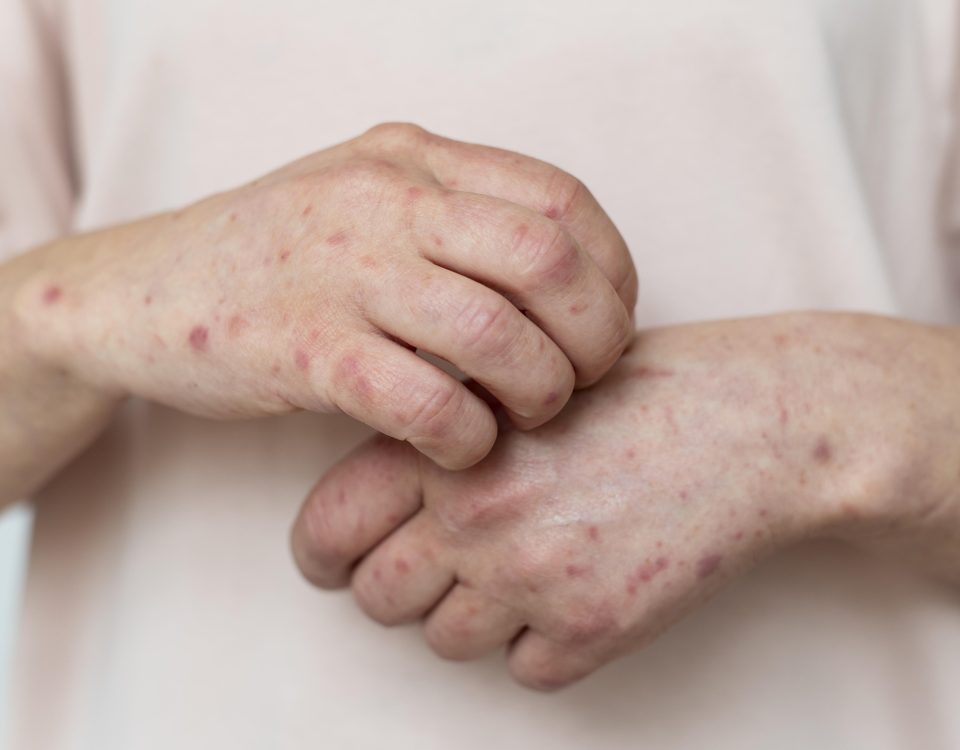
What Is Eczema?
26 March 2025
Top Benefits of Laser Genesis for Skin Rejuvenation in Edgewater, NJ
3 May 2025What Is Cellulitis?

Cellulitis is a common but potentially serious bacterial skin infection that can affect any part of the body. It occurs when bacteria enter the skin through cuts, abrasions, or cracks, leading to inflammation, swelling, and pain. If left untreated, cellulitis can spread rapidly, causing severe complications such as abscesses, tissue damage, and even bloodstream infections.
What is cellulitis, what causes it, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options together with preventive measures to help you understand and control this condition appropriately.
What are the causes of cellulitis?
Cellulitis is mainly caused by bacteria. The most common bacteria causing the disease are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. These bacteria penetrate the skin through:
- Cuts and wounds – Even minor cuts or insect bites can be entry points for the bacteria.
- Surgical wounds – If they are not cleaned and cared for, post-operative wounds are vulnerable.
- Skin conditions – Such as eczema, athlete's foot, or psoriasis can open up holes in the skin.
- Animal or human bites – These instigate the transfer of bacteria directly to the skin.
- Weak immune system – Anyone with diabetes, cancer, or HIV is at greater risk.
- Chronic swelling (lymphedema) – this will increase the risk of cellulitis through tissue fluid buildup.
Cellulitis Symptom
The symptoms can range from mild to severe. The common signs are:
- Redness and swelling – The area affected is red, hot, and swollen.
- Pain and tenderness – The affected skin may be tender to the touch or painful.
- Fever and chills – In some cases, there are associated flu-like symptoms with cellulitis.
- Blisters or pus formation – In the most severe cases, there might be abscesses filled with pus.
- Orange peel texture or skin dimpling – This could be a sign of deeper tissue involvement.
- Rapid spread of redness – If the infection spreads rapidly, medical attention is required immediately.

How Is Cellulitis Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses cellulitis through:
Physical Examination – Checking the affected area for redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness.
Medical History – Asking about recent injuries, surgeries, or existing health conditions.
Blood Tests – To assess for signs of infection, mostly in severe ones.
Wound Culture – An open wound or abscess, a sample will be taken into the lab for testing.
Imaging Tests, in rare cases – Ultrasound or MRI in assessing deeper infections.
Cellulitis Treatment Choices

Cellulitis is considered a medical disease and should therefore be treated earlier. The initial treatments are;
Antibiotics
- Oral antibiotics – Mild to moderate cellulitis is typically treated with oral antibiotics, such as cephalexin, dicloxacillin, or clindamycin.
- Intravenous (IV) antibiotics – In more serious cases, a hospital stay is needed to treat with IV antibiotics.
- Duration – Therapy usually is given for 7 to 14 days; more severe infections might require longer.
Pain Management
- Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Applying cold compresses may reduce discomfort and swelling.
Wound Care Tips & Cosmetic Treatment Considerations:
-
Keeping the wound clean and properly dressed helps prevent further infection.
-
Elevating the affected limb can reduce swelling and support faster healing.
-
If you're undergoing any cosmetic treatments such as chemical peels Hydrafacial or RF microneedling , remember that your skin may be extra sensitive during recovery.
-
In such cases, it's crucial to follow Hydrafacial aftercare guidelines strictly to avoid irritation or secondary infection, especially when the skin barrier is already compromised.
-
Many people also like to check the cost of RF microneedling before booking a session to ensure it fits within their skincare budget.
Hospitalization (For Severe Cases)
- If oral antibiotics fail to improve the condition or trigger complications, then hospitalization is necessary.
- If an abscess develops, a need for surgical drainage may be necessary.
How to Avoid Cellulitis
Prevention helps keep one at bay with cellulitis. Here are some crucial steps for protection against this:
- Keep hygiene in check – Wash your hands often and clean your skin.
- Treat your skin wounds quickly – Clean any cuts, scrapes, or bites and put on an antibiotic ointment.
- Moisturize the skin – Dry or cracked skin is more likely to become infected.
- Control chronic conditions – If you have diabetes or lymphedema, try to keep the condition under control.
- Wear protective clothing – If working in environments with risks of cuts or bites, wear appropriate protective gear.
- Avoid scratching insect bites or rashes – This can create an opening for bacteria.
- Regularly check your feet – Diabetic individuals should inspect their feet daily for cuts, blisters, or infections.

Potential Complications of Cellulitis
If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to serious health complications, such as:
- Abscess formation – Pockets of pus can occur and will require surgical drainage.
- Sepsis (blood infection) – This is the very rare potential complication that occurs when cellulitis progresses to potentially life-threatening infections in the blood.
- Necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating disease) – A serious, potentially deadly bacterial infection characterized by rapid progression.
- Chronic swelling (lymphedema) – Permanent swelling may be present if the lymphatic vessels are damaged.
- Recurrent cellulitis – Some people have recurring episodes and thus need long-term preventive measures.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention immediately if any of the following occur:
- Redness area is spreading rapidly.
- Fever and chills.
- Painful or sore with severe tenderness.
- Blistering, black patches, or purulent discharge.
- Failure to improve by 48 hours on antibiotics.
Early medical intervention can prevent complications and hasten recovery.
Conclusion
Cellulitis is a severe infection of the skin caused by bacteria. It should be treated in the hospital with antibiotics. It is essential to know the causes, symptoms, and treatment of cellulitis so that it can be detected early and managed properly. Preventive measures such as good hygiene, proper wound care, and control of underlying conditions can reduce the risk of cellulitis.
If you suspect cellulitis, do not delay seeking medical advice. For more information on skincare and medical aesthetics visit Bergen Premier Aesthetics.